This model represents the two-way handshake mechanism of the IEEE 802.11 medium access control scheme, operating in a fixed network topology, using the modelling formalism of probabilistic timed automata. These models were taken from the Prism case studies here. A PLASMA Lab project file containing WLAN models and properties used for this experiment can be downloaded here.
Probability estimation
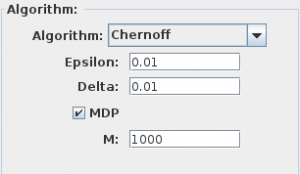
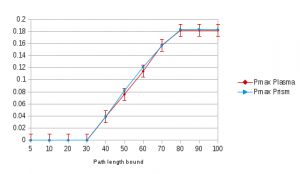
We estimated maximum and minimum probabilities using our Lightweight Monte Carlo Algorithm for MDPs and compared them to probabilities computed by PRISM. For this experiments we used our Chernoff bound with parameters Epsilon and Delta equal to 0.01 and M (the number of schedulers to test) set to a value of 1000. We used memoryless schedulers for this experiment.
The properties we used for our experiment were:
Important!
F<=#K col=2
With K ranging from 5 to 100.
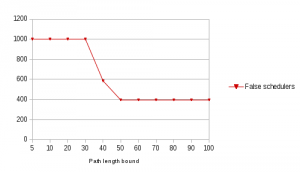
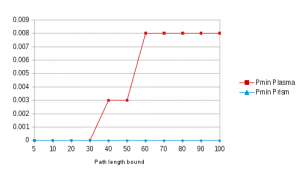 Our algorithm returns the minimum non-negative probability as Pmin, but also gives the total number of False schedulers, i.e. schedulers which cannot produce a positive trace.
Our algorithm returns the minimum non-negative probability as Pmin, but also gives the total number of False schedulers, i.e. schedulers which cannot produce a positive trace.
 Hypothesis testing
Hypothesis testing
We experiment the smart hypothesis testing algorithm by testing the models WLAN 5 and WLAN 6 with the following property:
Important!
F<=#100 col=2
We use the value 0.01 for the parameters alpha, beta and delta and report the results in the table below. Asterisks denote the true probability of the property. We give the results achieved with the minimum simulation budget.
| WLAN 5 | Proba | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| Budget | 500 | 1000 | * | 1000 | 1000 | 500 | |
| Time(s) | 0.8 | 2.6 | * | 2.9 | 2.9 | 1.3 | |
| WLAN 6 | Proba | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| Budget | 500 | 1000 | * | 2000 | 500 | 500 | |
| Time(s) | 1.3 | 2.2 | * | 6.5 | 1.3 | 1.3 |